40 nitrogenous bases
ACGT - Genome.gov ACGT is an acronym for the four types of bases found in a DNA molecule: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). A DNA molecule consists of two strands wound around each other, with each strand held together by bonds between the bases. Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine. Nitrogen Ammonia Nh3 Nitrite No2 And Nitrate No3 Ammonia is naturally present in most surface and wastewaters. Its further degradation to nitrites and nitrates consumes dissolved oxygen. Organic N-> NH3 +2 > NO2- +2 > NO3-. (3.15) Ammonia/Ammonium Ion (NH3/NH4+) In water, ammonia reacts as a base, raising the pH by generating OH- ions, as in Equation 3.16.
Vitamins are essential to any diet because User: a five-carbon sugar nucleotide 2. a giant molecule consisting of the sugar deoxyribose, phosphates, and nitrogen bases nitrogen base 3. a change in the genetic information code RNA 4. one of the three major types of chemicals making up a nucleotide in DNA deoxyribose 5. the combination of phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen bases in DNA...

Nitrogenous bases
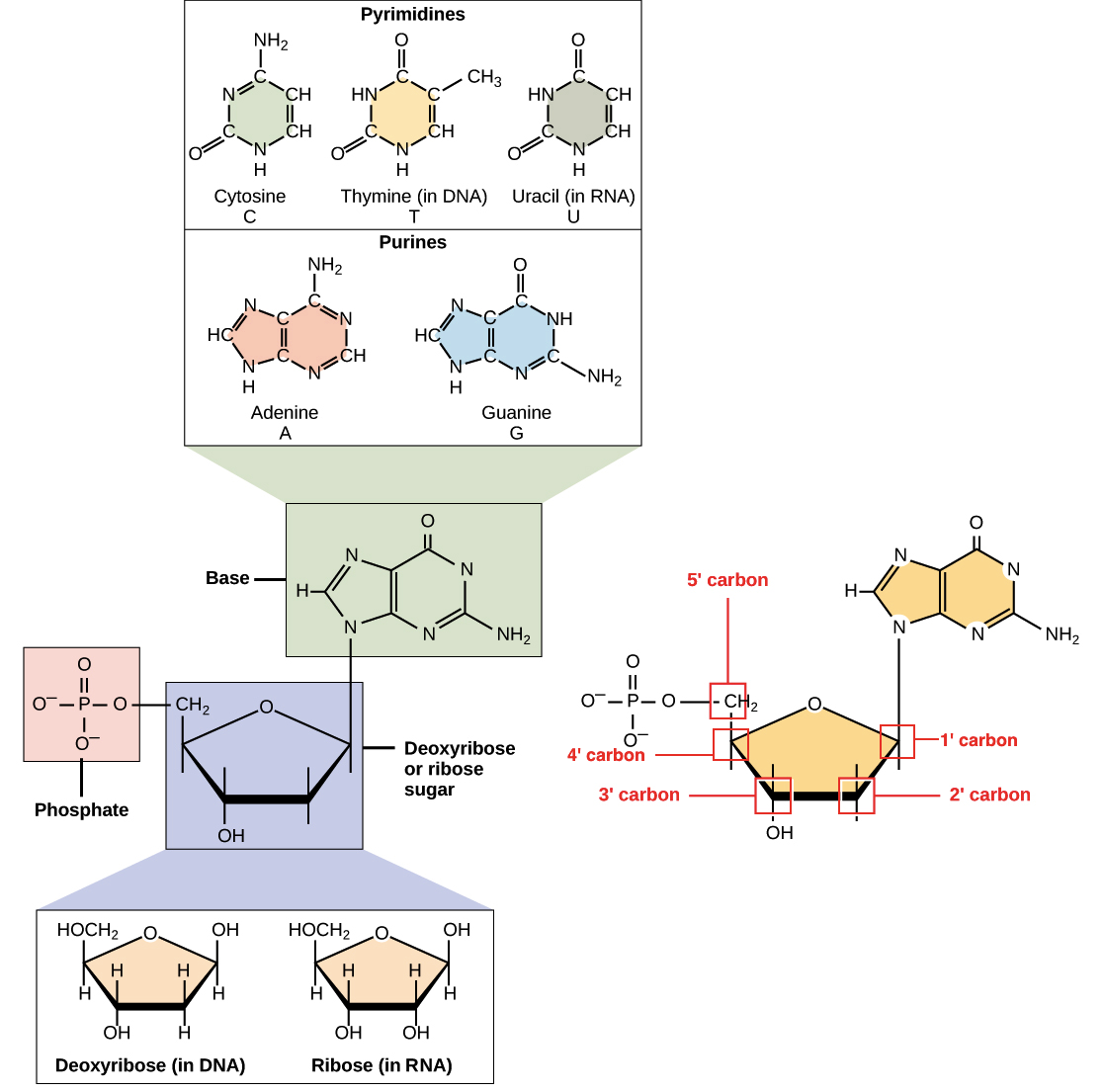
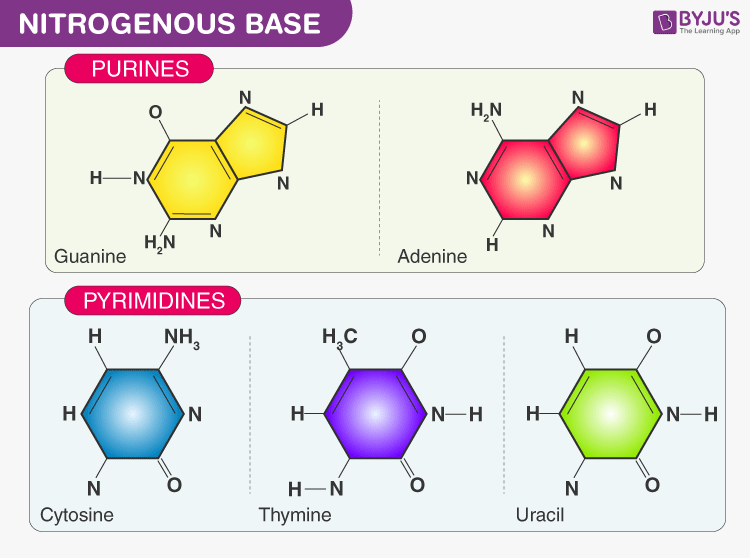
DNA Basics - BrainMass There are four possible bases: cytosine, adenine, guanine and thymine. Double helix formation is based on complementary base pairing rules where adenine and thymine are paired with two hydrogen bonds, whilst cytosine and guanine are paired with three hydrogen bonds. 10.1 Intermolecular Forces - Chemistry Each nucleotide contains a (deoxyribose) sugar bound to a phosphate group on one side, and one of four nitrogenous bases on the other. Two of the bases, cytosine (C) and thymine (T), are single-ringed structures known as pyrimidines. The other two, adenine (A) and guanine (G), are double-ringed structures called purines. Can we use Yeast nitrogen base without amino acids as a minimal media ... I can filtrate it with 0.45 micron but not with 0.22 micron. 3. I saw invitrogen protocol, it recommends that. "Dissolve 134 g of YNB with ammonium sulfate and w/o amino acids in 1L water" or ...
Nitrogenous bases. Albrecht Kossel | German biochemist | Britannica Albrecht Kossel, (born Sept. 16, 1853, Rostock, Mecklenburg [now Germany]—died July 5, 1927, Heidelberg, Ger.), German biochemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1910 for his contributions to understanding the chemistry of nucleic acids and proteins. He discovered the nucleic acids that are the bases in the DNA molecule, the genetic substance of the cell. Correct the following statements for mistakes, if any. (a) The four ... (a) The four nitrogenous bases in the DNA are Guanine, Thiamine, Adrenaline and Cytosine. (b) Genes are specific sequences of bases on a chromosome. (c) A nucleotide is composed of a sulphate, a sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base. (d) Nucleosomes are groups of cysteine molecules surrounded by DNA strands. What Are The 4 Bases Of DNA? - QuestionAnswer.io Four different types of nitrogenous bases are found in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, the thymine is replaced by uracil (U). … 1.5A). What are the 4 bases of DNA and how do they pair? Base Pair Attached to each sugar is one of four bases- adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), or thymine (T). How to pronounce nitrogenous base | HowToPronounce.com Easy. Moderate. Difficult. Very difficult. Pronunciation of nitrogenous base with 1 audio pronunciations. 1 rating.
Development of two types of intelligent indicators based on cellulose ... In this study, tracing paper (TP), which is made of cellulose fibers, was used as a base for the fabrication of freshness indicators using high (i.e., black carrot; C) and low (i.e., grape; G) acylated anthocyanins in order to track the freshness/spoilage of a variety of proteinous foods. The two anthocyanins were added to the TP by dipping method and color changes, chemical structure, and ... Replication - Genomics Actually, the nucleotides lining up by complementary base pairing are deoxynucleoside triphosphates, composed of a nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, and three phosphates. As the phosphodiester bond forms between the 5' phosphate group of the new nucleotide and the 3' OH of the last nucleotide in the DNA strand, two of the phosphates are removed ... 3.1 Formula Mass and the Mole Concept - Chemistry Acid-Base Equilibria. Introduction. 14.1 Brønsted-Lowry Acids and Bases. 14.2 pH and pOH. 14.3 Relative Strengths of Acids and Bases ... mass. One mole of glycine, C 2 H 5 O 2 N, contains 2 moles of carbon, 5 moles of hydrogen, 2 moles of oxygen, and 1 mole of nitrogen: The provided mass of glycine (~28 g) is a bit more than one-third the ... messenger RNA | Description & Function | Britannica messenger RNA (mRNA), molecule in cells that carries codes from the DNA in the nucleus to the sites of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm (the ribosomes). The molecule that would eventually become known as mRNA was first described in 1956 by scientists Elliot Volkin and Lazarus Astrachan. In addition to mRNA, there are two other major types of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA).
What is the similarities of DNA and RNA? - Blogsia Similarities: - DNA and RNA are made up of monomers called nucleotides. - DNA and RNA both contain pentose sugars. - DNA and RNA both have 3 nitrogenous bases: Adenine, Cytosine and Guanine. Click to see full answer. Herein, what is the similarities and differences of DNA and RNA? Similarity: Both are five-carbon pentose sugar which form nucleotides with base and phosphate (sugar + base ... Nucleic Acids Examples and Their Functions | New Health Advisor The many examples of nucleic acids including RNA (ribonucleic acid) and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) are composed of monomers called nucleotides. A nucleotide contains 3 components: a nitrogenous base, a phosphate group and a 5-carbon sugar. If the sugar is ribose, then its polymer is RNA. If it is deoxyribose, then its polymer is DNA. Learn about Nucleic Acids: Functions, Structure, Importance - EMBIBE 1) Nitrogen Bases: The nitrogenous components present in the nucleotide are called nitrogen bases. The five nitrogenous bases are derived from two types of heterocyclic bases such as - purine and pyrimidine. a) Purines are double ring bases. The two principal purine bases found in DNA and RNA are adenine (A) and guanine (G). Screenshot_20220704_071330.jpg - II" II" 7.l3 £9 {9 (D g... Screenshot_20220704_071330.jpg - II" II" 7.l3 £9 {9 (D g Biologicol Molecules GO TO 77 OF 103 EXPLANATION How many nitrogenous bases are there in
Model Dna Activity Replication Answers Suppression of ATR activity facilitates The DNA that makes up a single human chromosome might be made up of more than 250 million nucleotides com the PAPER CLIP DNA REPLICATION ACTIVITY ANSWERS book, also in various other countries or cities elongation, 6 Model Questions for GATE BT 2016, GATE XL 2016 Exan Model Questions for GATE BT 2016, GATE XL 2016 Exan.
Stages of Transcription | Concise Medical Knowledge - Lecturio The "rungs" of the ladder are made of matched nitrogen-containing molecules called nucleotides , frequently referred to as " bases ." DNA base pairs: Guanine (G), cytosine (C), adenine (A), and thymine (T) G pairs with C (and vice versa) via 3 hydrogen bonds. A pairs with T (and vice versa) via 2 hydrogen bonds.
Structure of DNA: Double Helical/Helix DNA Structure - Embibe There are two types of nitrogenous bases, namely Purines (Adenine and Guanine) and Pyrimidines (Cytosine, Uracil and Thymine). Nitrogenous base is linked to pentose sugar to form an nucleoside such as adenosine or deoxyadenosine, guanosine or deoxy guanosine, cytidine or deoxycytidine and uridine or deoxythymidine.
DNA And RNA Structure Test Quiz! - ProProfs DNA and RNA are the essential molecules in cell biology. They help with keeping and reading genetic information that exemplifies all life. They are both linear polymers consisting of sugars, phosphates, and bases. You must take this quiz on DNA and RNA and learn interesting trivia the most fun way. 1.
19.1: Nucleotides - Chemistry LibreTexts The nitrogenous bases found in nucleotides are classified as pyrimidines or purines. Pyrimidines are heterocyclic amines with two nitrogen atoms in a six-member ring and include uracil, thymine, and cytosine. Purines are heterocyclic amines consisting of a pyrimidine ring fused to a five-member ring with two nitrogen atoms.
Nitrogen - Wikipedia Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form N 2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas.
Practice Protein Codons And Answers Synthesis com The "language" that translates the sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA (mRNA) into the amino acids of a protein Practice Protein Synthesis Answer KeyProtein Synthesis Test Prep | Other Quiz - Quizizz Protein Synthesis Practice Problems Name: _____ Per: _____ Date: _____ Directions: For each of the following questions, transcribe the DNA ...
Unlike DNA, RNA A. has deoxyribose as the sugar within its nucleotide ... User: Unlike DNA, RNA A. has deoxyribose as the sugar within its nucleotide components. B. contains two strands wrapped in a helix. C. contains nitrogenous bases. D. pairs uracil with adenosine instead of thymine. Weegy: Unlike DNA, RNA pairs uracil with adenosine instead of thymine. Expert answered|Score 1|matahari|Points 57857| User: In which phase will crossing-over occur?
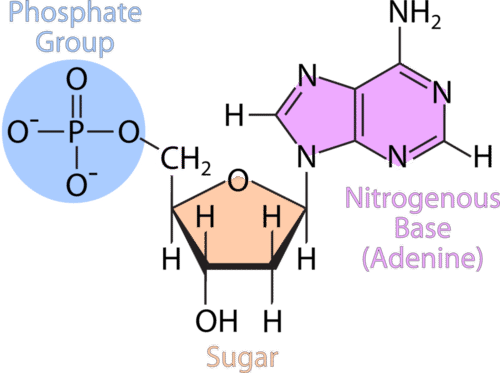
Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T). In RNA, the base uracil (U) takes the place of thymine.
Biochemistry, DNA Structure Article - StatPearls These nitrogenous bases are covalently bonded via a nitrogen atom to the 1' carbon of the deoxyribose sugar in a nucleotide (Figure 1a). [1] Although four major nitrogenous bases make up the nucleotides of DNA, other uncommon non-primary or modified bases have been found to exist in nature. [14]
DNA vs. RNA (Video & Fact Sheet) - Mometrix DNA is a polymer that has a deoxyribose and phosphate foundation with four nitrogenous bases: adenine and guanine (which are purine) and cytosine and thymine (which are pyrimidine). Now, Adenine only pairs with Thymine, and Guanine only pairs with Cytosine. DNA is a double helix structure and looks sort of like a spiraling staircase.
DNA - Wikipedia The nitrogenous bases of the two separate polynucleotide strands are bound together, according to base pairing rules (A with T and C with G), with hydrogen bonds to make double-stranded DNA. The complementary nitrogenous bases are divided into two groups, pyrimidines and purines.
Can we use Yeast nitrogen base without amino acids as a minimal media ... I can filtrate it with 0.45 micron but not with 0.22 micron. 3. I saw invitrogen protocol, it recommends that. "Dissolve 134 g of YNB with ammonium sulfate and w/o amino acids in 1L water" or ...
10.1 Intermolecular Forces - Chemistry Each nucleotide contains a (deoxyribose) sugar bound to a phosphate group on one side, and one of four nitrogenous bases on the other. Two of the bases, cytosine (C) and thymine (T), are single-ringed structures known as pyrimidines. The other two, adenine (A) and guanine (G), are double-ringed structures called purines.
DNA Basics - BrainMass There are four possible bases: cytosine, adenine, guanine and thymine. Double helix formation is based on complementary base pairing rules where adenine and thymine are paired with two hydrogen bonds, whilst cytosine and guanine are paired with three hydrogen bonds.











/purine-and-pyrimidine-nitrogenous-bases---skeletal-chemical-formulas-475632152-d34de0fec4e14f108a3e32901a1386c8.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/thymine-nucleobase-molecule-545861475-58692a3c5f9b586e02d03359.jpg)
















Post a Comment for "40 nitrogenous bases"