44 draw and label atp molecule
Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing Expert Answer. ANSWER : 1. During hydrolysis, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule broken down its one phosphate group to release chemical energy …. 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. Draw and label a diagram of the process of aerobic respiration. Include ... Draw an ATP molecule and describe its function within the cell. Give descriptions of photosynthesis and aerobic respiration. Describe how these two processes are linked between plants and animals based on the reactants and products (water, carbon dioxide, glucose, and oxygen) of both pathways.
ATP structure + function - Weebly The ATP molecule is hydrolsed into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate ion with the release of chemical energy. Every mole of ATP that is ...
Draw and label atp molecule
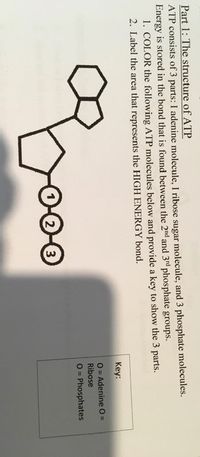
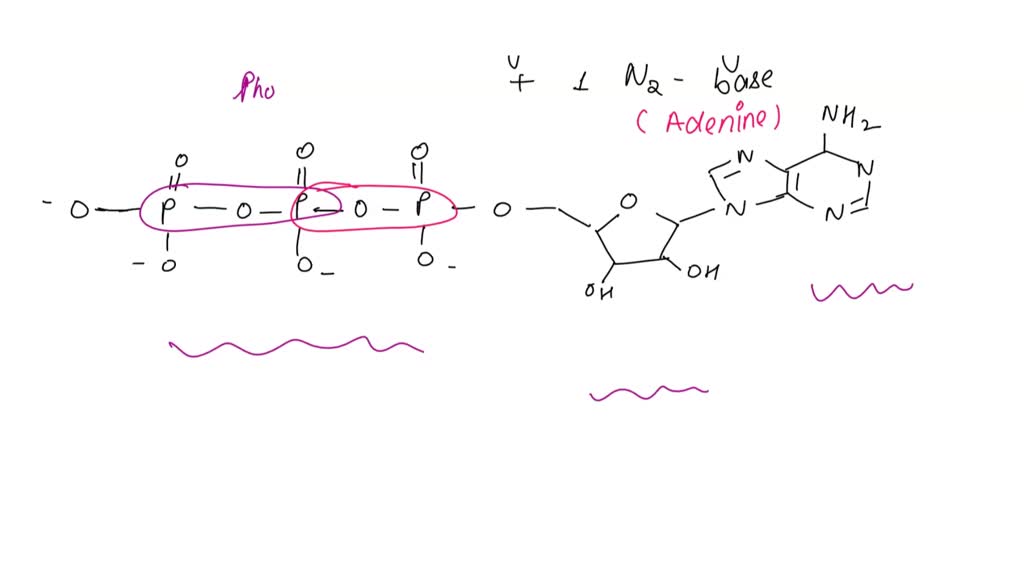
CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc. Ribose P Adenine P Bell Ringer 1 Draw and label the ATP - slidetodoc.com Bell Ringer: 1. Draw and label the ATP Molecule 2. What does ATP stand Ryan Barker - Photo and Resp Review.pdf - Cellular... Draw and label the ATP molecule 2. How does ATP release energy? 3. Define heterotrophs and provide an example of each. 4. Define autotrophs and provide an example of each. 5. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis. 6. Where do the light-dependent reactions take place? 7.
Draw and label atp molecule. ATP and Sources of Energy.pptx on emaze Draw and label an ATP molecule; Specific Sugar ; Phosphate ; Specific Nitrogenous Base; Draw and label ATP cycle; Check out my latest presentation built on emaze.com, where anyone can create & share professional presentations, websites and photo albums in minutes. @emaze_tweets is the leading online #presentation software. ... Intermolecular Interactions: A) Draw ATP molecule and show electron ... A) Draw an ATP molecule and show electron pushing as a result of its hydrolysis reaction of ATP to ADP in the presence of H{eq}_2 {/eq}O. B) Draw non-cyclic (linear) glucose, and label one electrophile and one nucleophile group within that molecule. Model of ATP Molecule - Perkins School For The Blind The model described is of a molecule of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which is the energy currency of the cell because it provides energy for the cell's ... 1. Label the parts of the ATP molecule using the word bank. What is formed when you break a bond between phosphate groups in ATP? 4. How many TOTAL molecules of ATP are produced during the process of cellular respiration ...
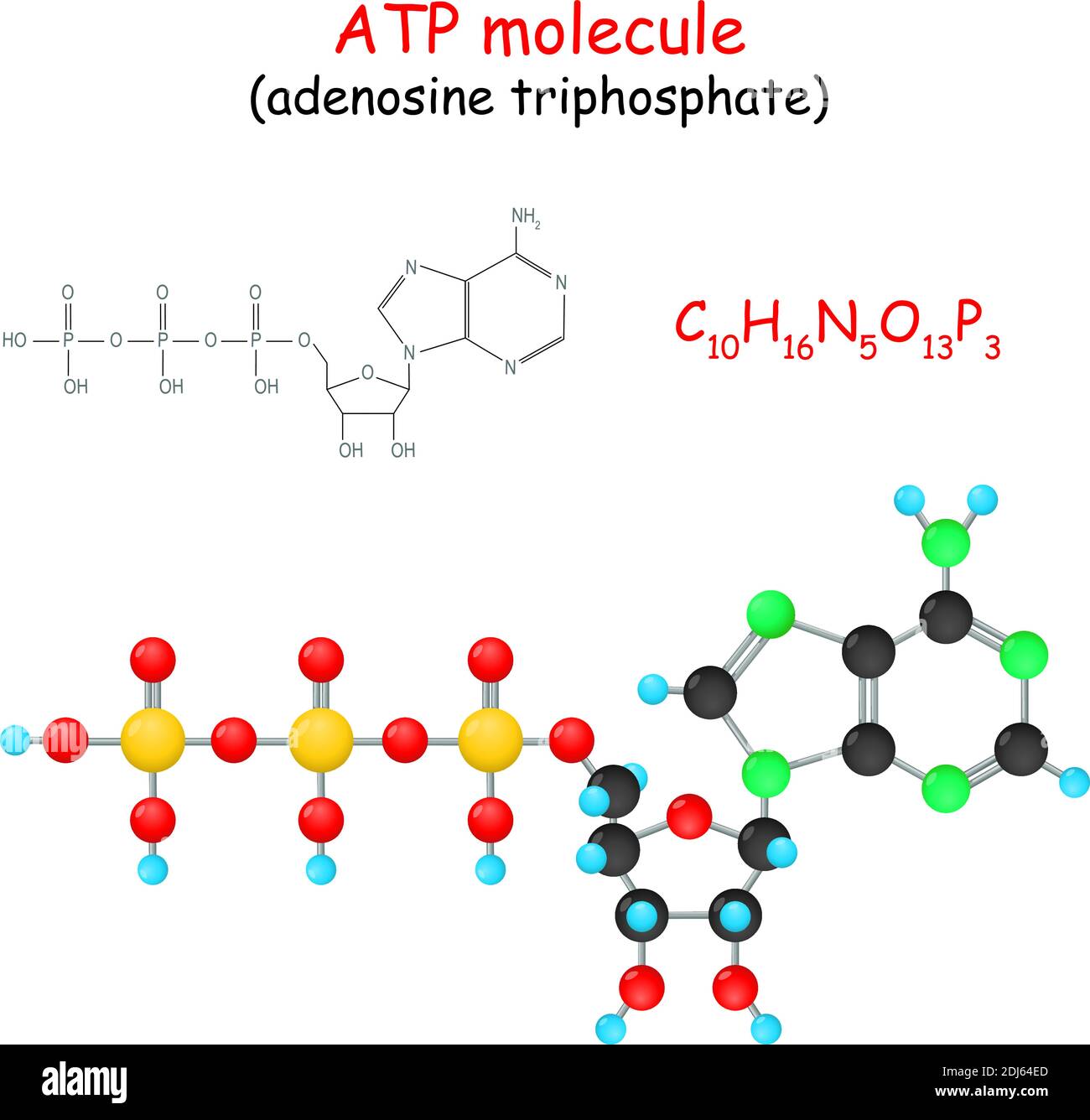
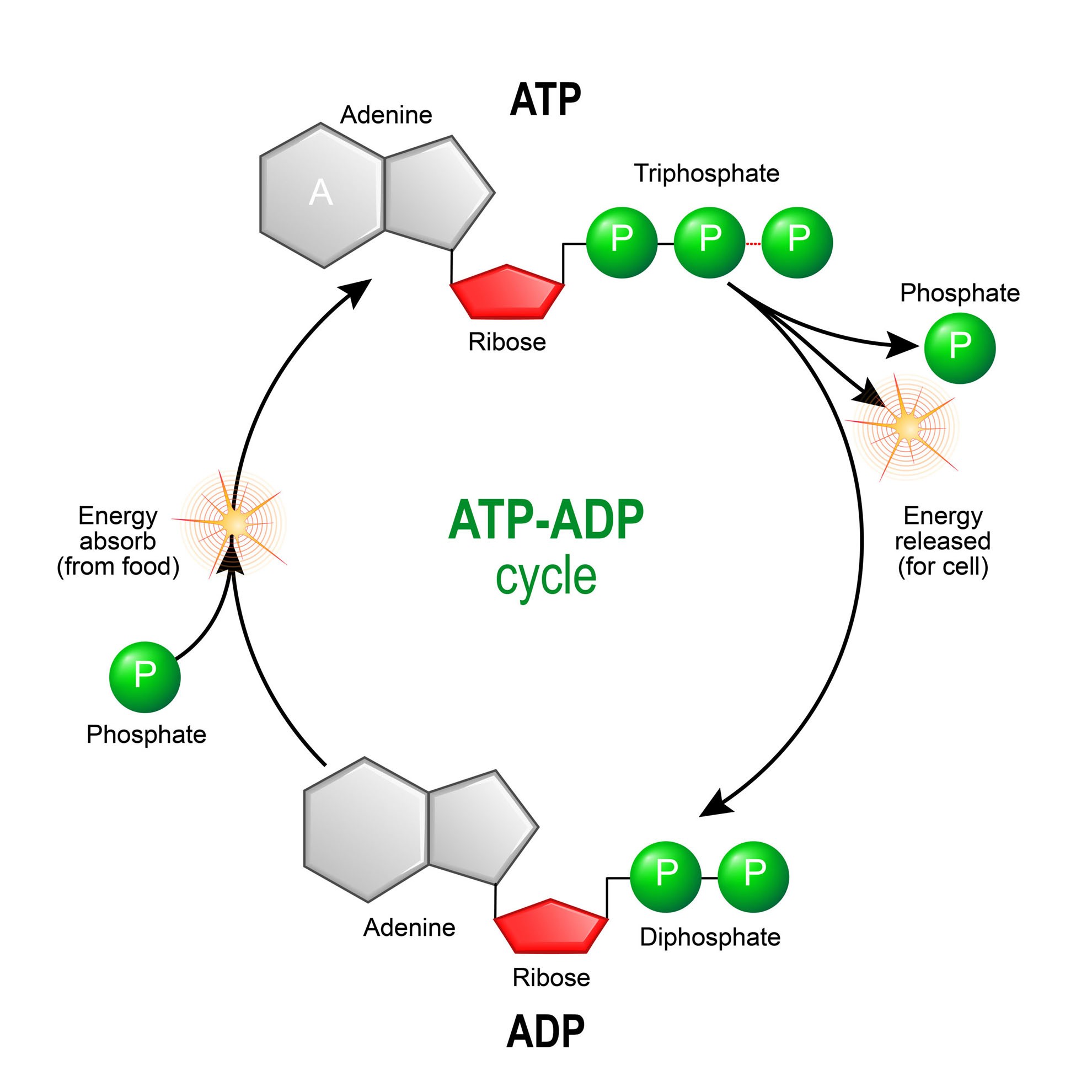
8.1: ATP - Biology LibreTexts An important chemical compound is adenosine triphospate ( ATP ). The main cellular role of ATP is as a "short-term" energy transfer device for the cell. The hydrolysis reactions that liberate one or more of ATP's phosphates are exergonic and many, many cellular proteins have evolved to interact with ATP in ways that help facilitate the transfer ... 1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain (in diagrams) how energy can be \"stored\" using ADP and a phosphate group.. . 3. Use diagrams to illustrate how energy is released from ATP molecules.. . 4. What is \"left over\" when energy is released from ATP?. ... Now, the ATP molecule has a head and tail, ... ATP | Learn Science at Scitable - Nature ATP. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate, or ATP, is the principal molecule for storing and transferring energy in cells. It is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell and can be compared to ... Adenosine-5'-triphosphate | C10H16N5O13P3 - PubChem ATP is an adenosine 5'-phosphate in which the 5'-phosphate is a triphosphate group. It is involved in the transportation of chemical energy during metabolic pathways. It has a role as a nutraceutical, a micronutrient, a fundamental metabolite and a cofactor. It is an adenosine 5'-phosphate and a purine ribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate.
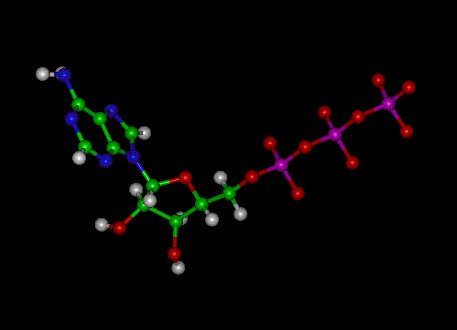
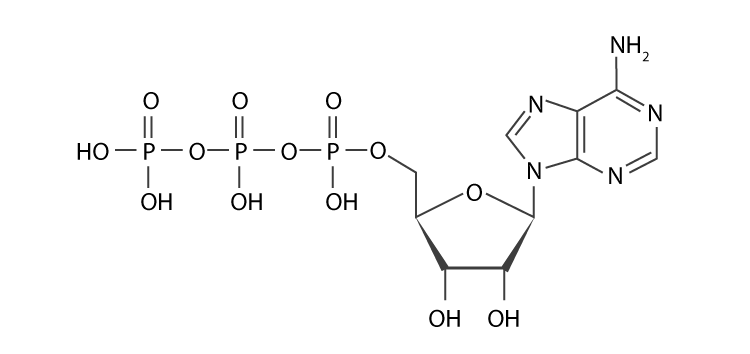
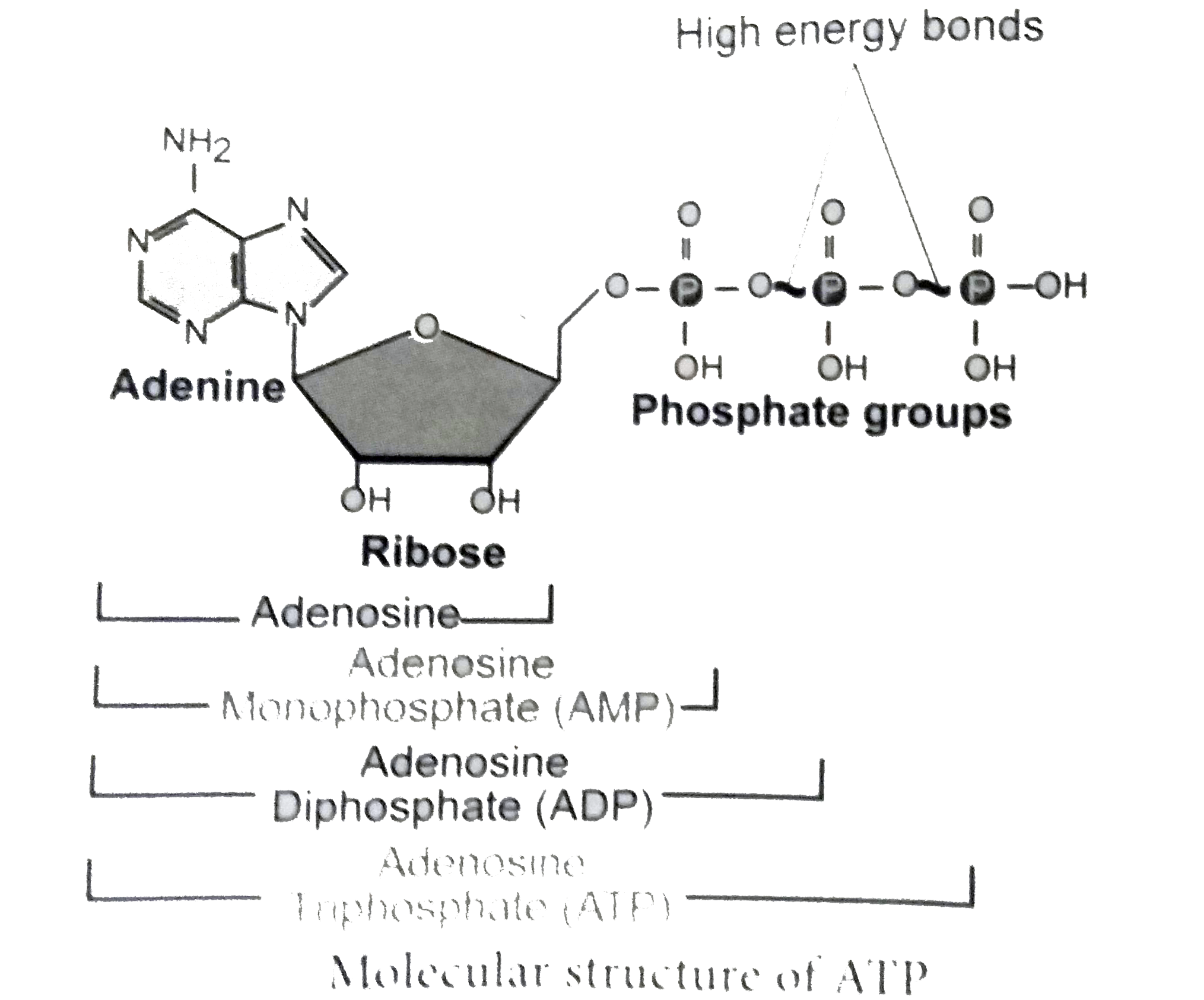
Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and ... 7.6: ATP as Energy carrier - Chemistry LibreTexts ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy currency for cellular processes. ATP provides the energy for both energy-consuming endergonic reactions and energy-releasing exergonic reactions, which require a small input of activation energy. When the chemical bonds within ATP are broken, energy is released and can be ... Label the molecule of ATP. Show where the high energy bond is ... The ATP molecule is comprised of an adenosine molecule attached to three phosphates. The bond with the last phosphate is highly energetic. The ATP Molecule -Chemical and Physical Properties - World of Molecules The Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. Energy is released by hydrolysis of the third phosphate group.
ATP Diagram | Quizlet Start studying ATP. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Start studying ATP. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. ... a high energy molecule that transfers energy in cells. ADP (function) a lower-energy molecule that can be converted into ATP. Tri. three. Di ...
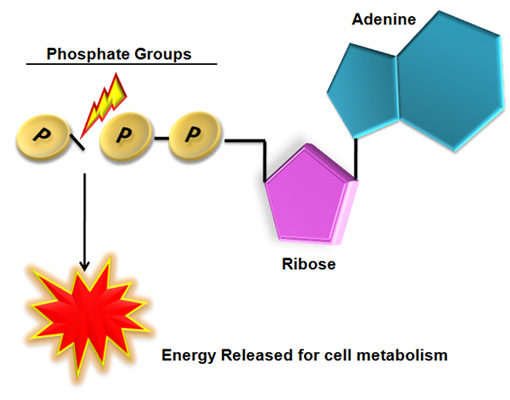
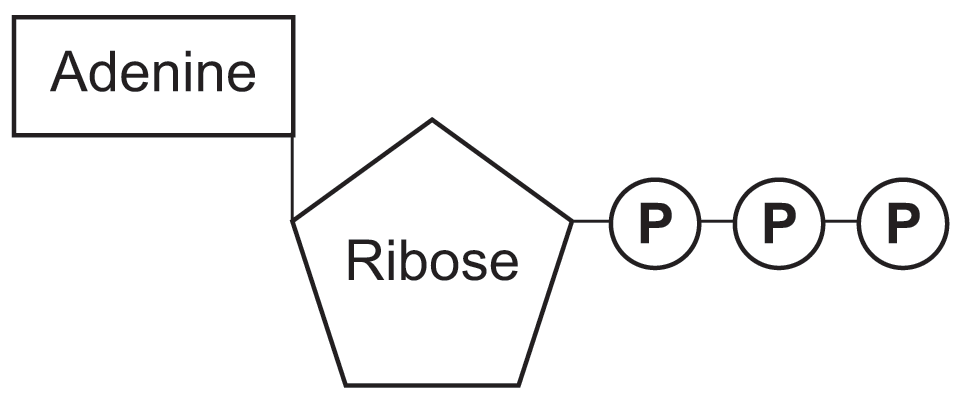
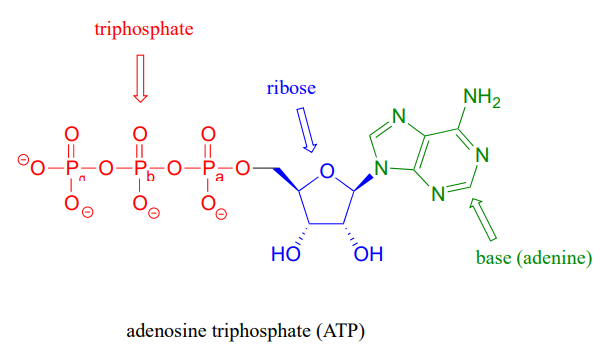
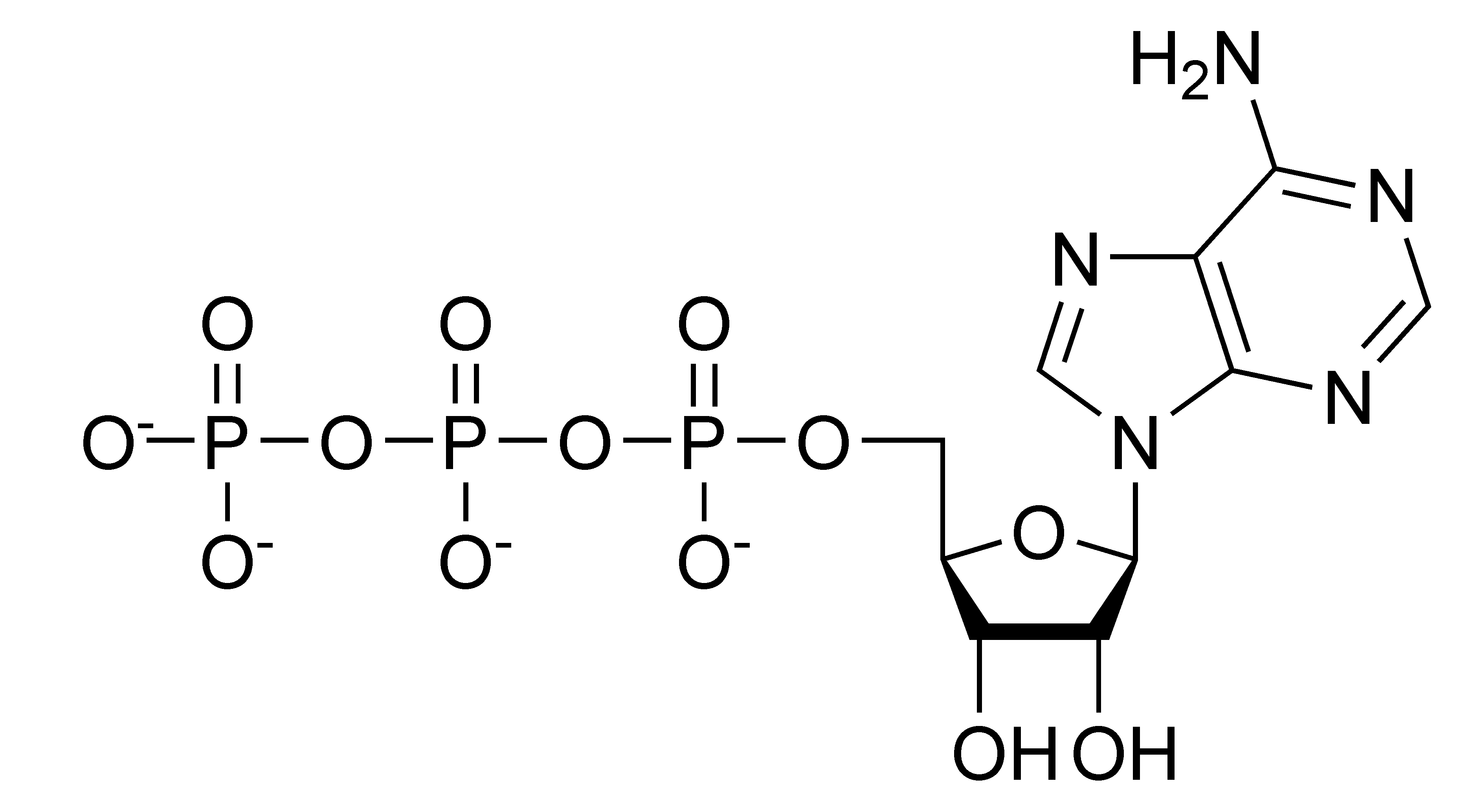
Draw an ATP molecule and describe its function within the cell. Adenosine triphosphate consists of an adenosine molecule bound to three phosphate molecules. A diagram of an adenosine triphosphate compound.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP.
SOLVED: Draw and Iabel an ATP molecule Using ... - Numerade May 23, 2022 ... In the first question, it is asked to draw the structure and the bonds. So first of all, ... Label the atoms on the ATP molecule.
ATP Definition and Importance in Metabolism - ThoughtCo Updated on May 09, 2019. Adenosine triphosphate or ATP is often called the energy currency of the cell because this molecule plays a key role in metabolism, particularly in energy transfer within cells. The molecule acts to couple the energy of exergonic and endergonic processes, making energetically unfavorable chemical reactions able to proceed.
Draw the structure of ATP molecule. - Doubtnut Jun 27, 2022 ... Watch complete video answer for “Draw the structure of ATP molecule.” of Biology Class 11th. Get FREE solutions to all questions from ...
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The discovery of ATP was made by Karl Lohman (1929). ATP is a nucleotide consisting of a base-adenine, a pentose sugar-ribose and three phosphate groups. Out of three phosphate groups the last two are attached by high energy rich bonds (Figure 14.3). On hydrolysis, it releases energy (7.3 K cal or 30.6 KJ/ATP) and it is found in all living ...
Solved 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and - Chegg Question: 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and label the adenine, ribose, and three phosphates. 2) Discuss ATP's function as an energy molecule. Specifically discuss: how many phosphate groups would need to be removed from ATP to create the following molecules: Adenosine, AMP, and ADP. how energy is released when a molecule of ATP loses one or
Atp Molecule Illustrations, Royalty-Free Vector Graphics & Clip Art Choose from Atp Molecule stock illustrations from iStock. Find high-quality royalty-free vector images that you won't find anywhere else.
What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic Explanation: ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine. Ribose. Three Phosphate Groups. Here is a picture:
Chapters 5b - 7 Honors Biology Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label an ATP molecule. Be able to identify the adenosine part, and 3 phosphate groups. Identify and label the high energy bonds. ... An organelle found in BOTH plants and animals which produces ATP (energy molecule) Structure: Double membrane-bound sac with flattened sacs inside. C6H12O6. Chemical formula for Glucose 6 Carbons 12 ...
Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Answer: Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP. This occurs when a molecule of adenosine diphosphate (ADP) uses the energy ...
ATP: Definition, Structure & Function | StudySmarter The definition of ATP in biology. ATP or adenosine triphosphate is the energy-carrying molecule essential for all living organisms. It is used to transfer the chemical energy necessary for cellular processes. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy for many processes in living cells.
Physiology, Adenosine Triphosphate - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf The body is a complex organism, and as such, it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups. ATP is commonly referred to as the "energy currency ...
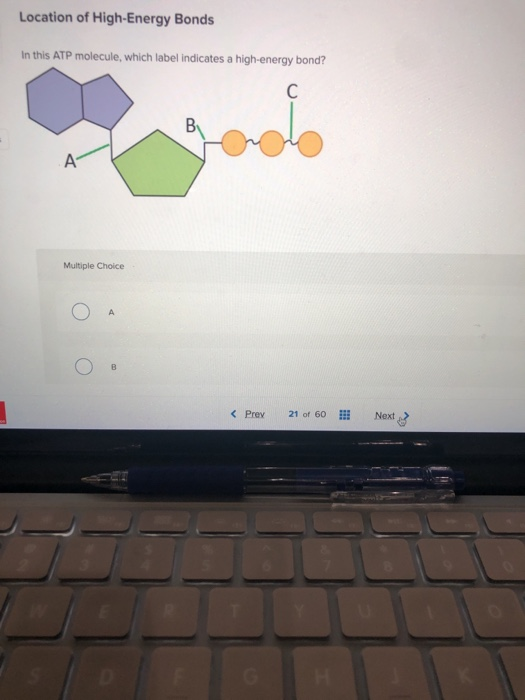
Answered: Draw the chemical structure of ATP 1.… | bartleby Science Biology Draw the chemical structure of ATP 1. Circle and label the following parts: Adenine, Ribose, Tri-Phosphate. 2. Put a bracket around and label the part that is called Adenosine. 3. Use nested brackets and labels to identify AMP, ADP and ATP 4. Use arrows to identify the high energy bonds
ATP: Adenosine triphosphate (video) | Khan Academy In contrast, the bond between a phosphoryl group and Adenosine is much lower in energy. These reactions: ATP + H₂0 → ADP + Pᵢ. ADP + H₂0 → AMP + Pᵢ. yield more than twice the energy compared to this reaction: AMP + H₂0 → Adenosine + Pᵢ. So, yes the additional phosphates result in higher energy bonds. Comment.
Adenosine triphosphate | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ...
ATP | Structure, Synthesis, Hydrolysis, Functions & Summary This energy is made available for cellular processes by ATP hydrolysis. The terminal two phosphate groups of ATP are linked to the rest of the molecule by high energy phosphate bonds. Each of these bonds releases 7.3 Kcal/mol of energy upon hydrolysis. The hydrolysis of ATP is a two-step process.
9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor ATP is a big molecule, but the bond-breaking and bond-forming events we will be studying in this chapter all happen in the phosphate part of the molecule. You will see structural drawings of ATP, ADP, and AMP abbreviated in many different ways in this text and throughout the biochemical literature, depending on what is being illustrated. ...
Ryan Barker - Photo and Resp Review.pdf - Cellular... Draw and label the ATP molecule 2. How does ATP release energy? 3. Define heterotrophs and provide an example of each. 4. Define autotrophs and provide an example of each. 5. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis. 6. Where do the light-dependent reactions take place? 7.
Bell Ringer 1 Draw and label the ATP - slidetodoc.com Bell Ringer: 1. Draw and label the ATP Molecule 2. What does ATP stand
CR Study guide.pdf - 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule.... 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy (including the enzyme responsible). 2. Why is ATP important? ATP is important because it supplies energy for our cells; without it we would not have the energy to grow, move, etc. Ribose P Adenine P
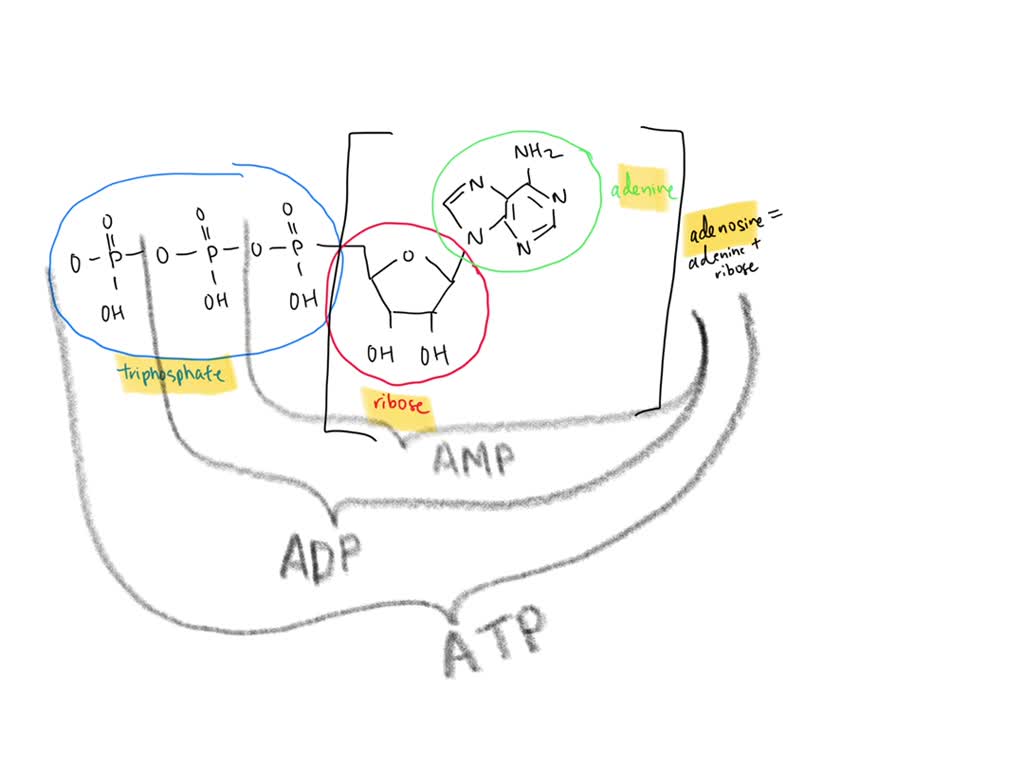
Part B, Draw the chemical structure of ATP, 1. Circle and label the following parts: Adenine, Ribose, Tri-Phosphate., 2. Put a bracket around and label the part that is called Adenosine., 3. Use ...
























![Identify the three components [(i),(ii) and (iii)] of ATP ...](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/887889_ba7e3b5cc09d418996079c2f5db4b569.png)

Post a Comment for "44 draw and label atp molecule"